Understanding Cloud Service Models: IaaS vs PaaS vs SaaS
Let’s talk about one of the most revolutionary tech trends that’s shaking up the business world today – Cloud Computing! When it comes to the cloud, do you ever feel lost in the fog of tech jargon? Not anymore! We’re here to clear the air with your very own “cloud service models explained” guide. Buckle up as we dive into the three main types of cloud server service models – Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS).
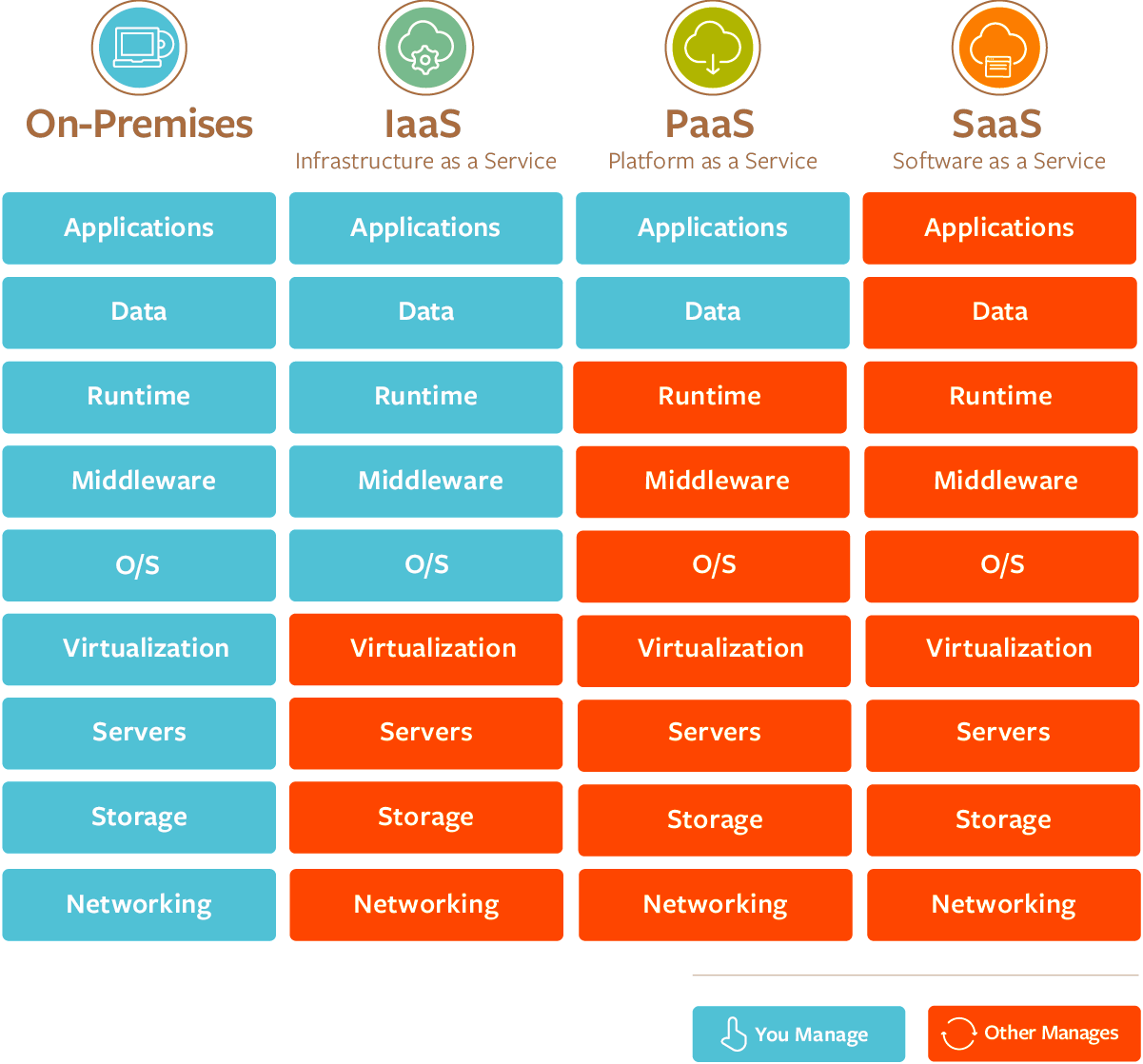
The Three Musketeers of the Cloud: IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS
Let’s make the “cloud service models explained” tour easier for you. Think of the three types of cloud service models as layers of a very modern, technologically advanced cake. At the base, we have IaaS. The middle layer? That’s PaaS. And the icing on top? It’s SaaS. Each layer has its own unique taste and purpose, yet they all work together to give you the full flavor of cloud computing.
The IaaS Layer: Your Very Own Virtual Toolbox
Do you like having control over your own tools and resources, but hate the idea of maintaining and managing all that hardware? IaaS might just be the answer to your prayers.
IaaS is like a virtual toolbox, complete with servers, storage, and networking resources. It’s one of the different cloud service models that allows businesses to rent these resources on an as-needed basis. This way, they only pay for what they use. With IaaS, the cloud provider takes care of all the heavy lifting involved in maintaining the infrastructure, leaving you free to focus on your core business.
The PaaS Layer: The Ideal Launchpad for Your Apps
Moving up the layers of cloud service models, we come to PaaS. Think of it as a high-tech launchpad for your apps.
PaaS is perfect if you’re a developer who wants to create and manage applications without the stress of handling the underlying infrastructure. With this type of cloud service models, you’re provided with a platform including operating system, database, and development tools. That means you can focus on the fun part – writing and managing your code – while your cloud provider takes care of the rest.
The SaaS Layer: Ready-to-Use Software in a Click
And finally, the icing on our cloud cake, SaaS. This is where cloud service models really start to shine for end-users.
SaaS is the delivery of ready-to-use software over the internet. It’s like subscribing to your favorite streaming service, but for software. You don’t need to worry about installations or updates; your cloud provider takes care of everything. All you need to do is login and start using your favorite software, whether that’s an email service, CRM, or project management tool.
With SaaS as one of the types of cloud service models, businesses can save money on software licensing, installation, and maintenance. Plus, it’s a great way to ensure you always have the latest version of your software.
Before diving into the detailed breakdown of IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS, it’s important to understand that these three cloud service models each offer distinct advantages depending on the specific needs of your business. Whether you’re looking for complete infrastructure control, a platform to develop applications, or software ready to use out of the box, these models are designed to provide scalable and cost-effective solutions. Let’s explore each of these models in detail to understand how they work and how they can benefit your business.
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
What is IaaS?
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) is the most basic and flexible cloud service model. In this model, cloud providers offer virtualized computing resources over the internet. Essentially, IaaS provides the building blocks for cloud IT, allowing you to rent infrastructure – servers, virtual machines, storage, networks, and operating systems – on a pay-as-you-go basis.
Key Features of IaaS
- Complete control over infrastructure
- Scalability and flexibility
- Pay-per-use pricing model
- Reduced hardware costs
- Access to enterprise-grade infrastructure
When to Use IaaS
IaaS is ideal for scenarios where you need maximum control over your IT resources but want to avoid the capital expenses and complexity of maintaining physical servers and infrastructure. Some common use cases include:
- Startups and small companies that want to avoid investing in hardware
- Larger companies looking to retain complete control over their applications and infrastructure
- Organizations experiencing rapid growth and needing to scale hardware quickly
- Temporary or experimental projects requiring quick setup and teardown of test environments
Examples of IaaS Providers
Some popular IaaS providers include:
- Amazon Web Services (AWS) EC2
- Microsoft Azure Virtual Machines
- Google Compute Engine
- DigitalOcean Droplets
Pros and Cons of IaaS
Pros:
- Maximum flexibility and control
- Cost-effective for variable or unpredictable workloads
- Easy scalability
- Pay only for what you use
Cons:
- Requires technical expertise to manage and maintain
- Security responsibilities shared between provider and user
- Potential for unexpected costs if not managed properly
Platform as a Service (PaaS)
What is PaaS?
Platform as a Service (PaaS) is a cloud computing model that provides a platform allowing customers to develop, run, and manage applications without the complexity of maintaining the underlying infrastructure. PaaS includes infrastructure like IaaS, but also middleware, development tools, business intelligence (BI) services, database management systems, and more.
Key Features of PaaS
- Pre-configured development environments
- Built-in scalability and high availability
- Integrated database management and security features
- Automated updates and patch management
- Collaboration tools for development teams
When to Use PaaS
PaaS is particularly useful for scenarios where multiple developers are working on the same development project or where you want to efficiently manage the entire lifecycle of your applications. Some common use cases include:
- Development and testing environments
- Web application hosting
- Big data analytics
- Internet of Things (IoT) platforms
- API development and management
Examples of PaaS Providers
Some well-known PaaS providers include:
- Heroku
- Google App Engine
- Microsoft Azure App Service
- Red Hat OpenShift
Pros and Cons of PaaS
Pros:
- Faster time to market for applications
- Reduced complexity in application development and deployment
- Built-in tools and services for testing and deployment
- Easier collaboration for development teams
Cons:
- Limited control over underlying infrastructure
- Potential vendor lock-in
- May have limitations on which programming languages or frameworks can be used
Software as a Service (SaaS)
What is SaaS?
Software as a Service (SaaS) is a cloud computing model where software applications are provided over the internet on a subscription basis. Instead of installing and maintaining software, you simply access it via the internet, freeing yourself from complex software and hardware management.
Key Features of SaaS
- Web-based access to commercial software
- Software managed from a central location
- Users not responsible for hardware or software updates
- Pay-per-use pricing model
- Automatic updates and patch management
When to Use SaaS
SaaS is ideal for applications that are used by a wide range of users and don’t require extensive customization. Some common use cases include:
- Email and collaboration tools (e.g., Microsoft 365, Google Workspace)
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM) systems
- Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) software
- Human Resources Management (HRM) solutions
- Project management tools
Examples of SaaS Providers
Some popular SaaS providers and applications include:
- Salesforce (CRM)
- Dropbox (File storage and sharing)
- Slack (Team communication)
- Zoom (Video conferencing)
- QuickBooks Online (Accounting)
Pros and Cons of SaaS
Pros:
- No need for software installation or maintenance
- Accessible from any device with an internet connection
- Automatic updates and new features
- Predictable costs with subscription-based pricing
Cons:
- Limited customization options
- Dependence on internet connectivity
- Potential data security and privacy concerns
- Less control over features and functionality
Comparing IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS
Now that we’ve explored each cloud service model individually, let’s compare them side by side to highlight their key differences:
Level of Control
- IaaS: Highest level of control over infrastructure
- PaaS: Control over applications and hosting environment, but not underlying infrastructure
- SaaS: Least control, as the entire application is managed by the provider
Management Responsibilities
- IaaS: User manages operating systems, storage, and deployed applications
- PaaS: User manages deployed applications and, in some cases, hosting environment settings
- SaaS: User only manages data and access; everything else is managed by the provider
Customization
- IaaS: Highly customizable, as users have full control over the infrastructure
- PaaS: Customizable within the constraints of the platform
- SaaS: Limited customization options, typically through configuration settings
Scalability
- IaaS: Manual scaling of infrastructure resources
- PaaS: Often includes auto-scaling features for applications
- SaaS: Scaling is managed entirely by the provider
Use Cases
- IaaS: Ideal for organizations that want control over their infrastructure without managing physical hardware
- PaaS: Best for development teams focusing on application development without worrying about infrastructure
- SaaS: Perfect for businesses looking for ready-to-use software solutions with minimal management overhead
Choosing the Right Cloud Service Model
Selecting the appropriate cloud service model depends on various factors, including your organization’s technical expertise, resource requirements, budget constraints, and specific use cases. Here are some guidelines to help you make an informed decision:
Consider IaaS if:
- You need maximum control over your IT resources
- Your workloads are unpredictable or prone to rapid changes
- You have the technical expertise to manage and maintain infrastructure
- You want to migrate existing applications to the cloud with minimal modifications
Consider PaaS if:
- You want to focus on application development without managing infrastructure
- You need a platform that supports the entire application lifecycle
- You require built-in tools for testing, deployment, and scaling
- You want to reduce the complexity of database management and other middleware
Consider SaaS if:
- You need standard software applications with minimal customization
- You want to reduce IT management overhead
- You prefer predictable, subscription-based pricing
- You need applications that are accessible from anywhere on any device
Real-World Examples
To better illustrate how these cloud service models work in practice, let’s look at some real-world examples:
IaaS Example: E-commerce Platform
An e-commerce company experiences seasonal spikes in traffic during holidays. By using IaaS, they can easily scale their infrastructure up or down based on demand. During peak seasons, they can quickly add more servers to handle increased traffic, and scale back during slower periods to save costs.
PaaS Example: Mobile App Development
A startup is developing a new mobile app and wants to focus on creating innovative features rather than managing infrastructure. By using a PaaS solution, the development team can access pre-configured environments, integrated testing tools, and automatic scaling capabilities. This allows them to bring their app to market faster and more efficiently.
SaaS Example: Customer Relationship Management
A small business wants to improve its customer relationship management but doesn’t have the resources to develop and maintain its own CRM system. By subscribing to a SaaS CRM solution like Salesforce, they can access enterprise-grade CRM functionality without the need for in-house IT expertise or infrastructure.
The Future of Cloud Service Models
As technology continues to evolve, we’re seeing new trends emerge in the cloud computing space:
- Hybrid and Multi-Cloud Approaches: Many organizations are adopting a mix of different cloud service models and providers to meet their specific needs.
- Serverless Computing: This model, sometimes called Function as a Service (FaaS), takes the concept of PaaS even further by allowing developers to focus solely on writing code without worrying about any infrastructure management.
- Edge Computing: As IoT devices become more prevalent, edge computing is gaining traction, bringing computation and data storage closer to the location where it’s needed.
- AI and Machine Learning as a Service: Cloud providers are increasingly offering AI and ML capabilities as part of their service offerings, making these technologies more accessible to businesses of all sizes.
Conclusion
Understanding the differences between IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS is crucial for making informed decisions about your organization’s cloud strategy. Each model offers unique benefits and is suited to different use cases:
- IaaS provides the most flexibility and control but requires more management from your team.
- PaaS offers a balance between control and convenience, ideal for application development and deployment.
- SaaS provides ready-to-use software solutions with minimal management overhead.
As you evaluate your cloud computing needs, consider factors such as your technical expertise, desired level of control, scalability requirements, and budget constraints. Remember that many organizations use a combination of these models to create a comprehensive cloud strategy that meets their specific needs.
By leveraging the right cloud service models, you can improve your organization’s agility, reduce costs, and focus on what matters most – driving innovation and growth in your business.



